Naive RAG vs. advanced RAG: What are the differences?
Explore the key distinctions between naive RAG and advanced RAG, including how they differ in process, accuracy, scalability, performance & more.
In this article
Modern GenAI systems are built on a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) foundation.
RAG comes in many forms and varying levels of complexity. Some are simple and easy to use, while others are focused on scaling to the next level.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- What ‘naive’ and ‘advanced’ RAG mean, and how they are different from each other.
- The workings of both, from the most basic to the advanced steps.
- Practical insights into the major differences between the two.
- The best time to use them and their applications in real-world use cases.
- The most common benefits and challenges of each.
- The best practices to evolve from naive RAG to advanced RAG, and how you can use Meilisearch to simplify the process
By the end, you’ll know exactly which RAG setup fits your team’s specific situation and performance requirements.
What is naive RAG?
Naive RAG is the simplest type of RAG.
It involves a single retriever fetching relevant documents and passing them to a large language model for generation. It relies on vector similarity search, which in turn relies on embeddings and language models such as OpenAI or Sentence-BERT.
You see naive RAG daily, more than you realize. It’s in prototypes, chatbots, and internal tools designed to optimize latency and simplicity.
However, it’s not the go-to option for accuracy, unlike advanced RAG. Let’s look at that next.
What is advanced RAG?
When you want to take RAG to the next level, you arrive at advanced retrieval-augmented generation. It builds on the naive approach by adding more layers of precision and reliability through reranking, query rewriting, and multi-stage retrieval processes. This not only improves the accuracy of the generation but also provides final responses that users enjoy reading.
You can find advanced RAG in production environments where the primary focus is on accuracy and removing hallucinations. This is ideal for specific domains, such as finance or healthcare.
Now, let’s explore how each RAG system works in practice.
How does naive RAG work?
Naive RAG follows a simple three-step workflow connecting information retrieval and generation.
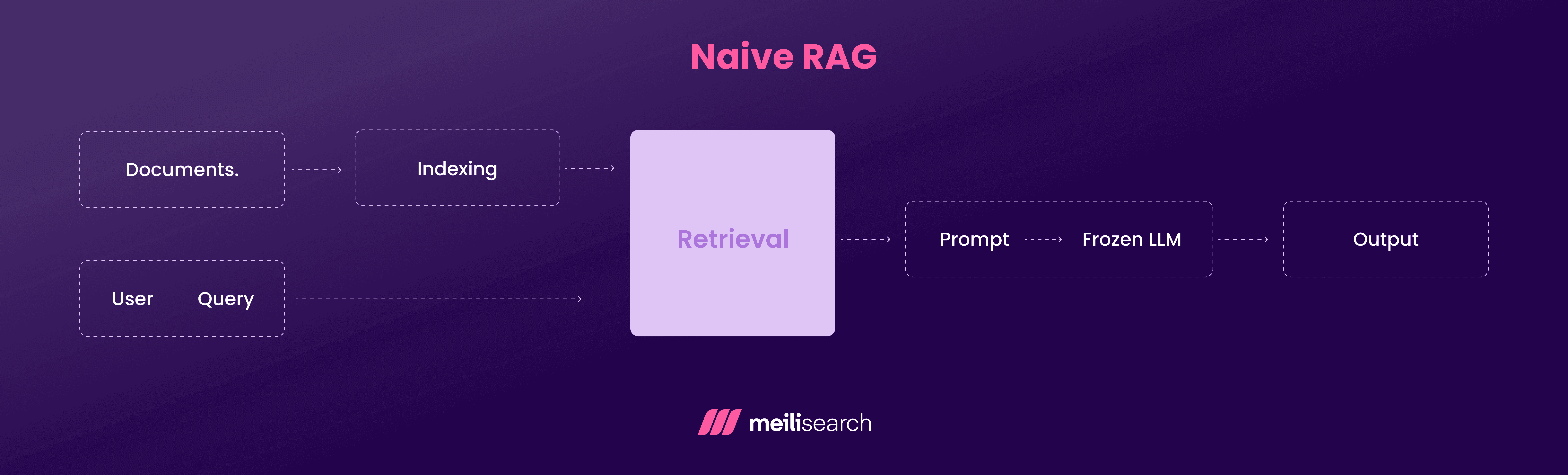
- Indexing: When indexing, the documents are first chunked into smaller sections. These smaller sections are then converted into vector embeddings through language models. Then, these vectors are stored in a vector database, such as Meilisearch or FAISS.
- Retrieval: Similar to document indexing, a user query is also converted into an embedding. The retriever then finds vectors similar to the query from the database using similarity metrics, such as cosine similarity.
- Generation: For each generation process, the retrieved documents are first linked and fed to a large language model (LLM). From the LLM, a response is generated based on the context provided.
Naive RAG prioritizes speed and simplicity. If you want a basic functionality or RAG deployment, this is the way to go.
Now, let’s see how advanced RAG works.
How does advanced RAG work?
Advanced RAG builds upon naive RAG through various optimization layers that enhance retrieval and generation quality.
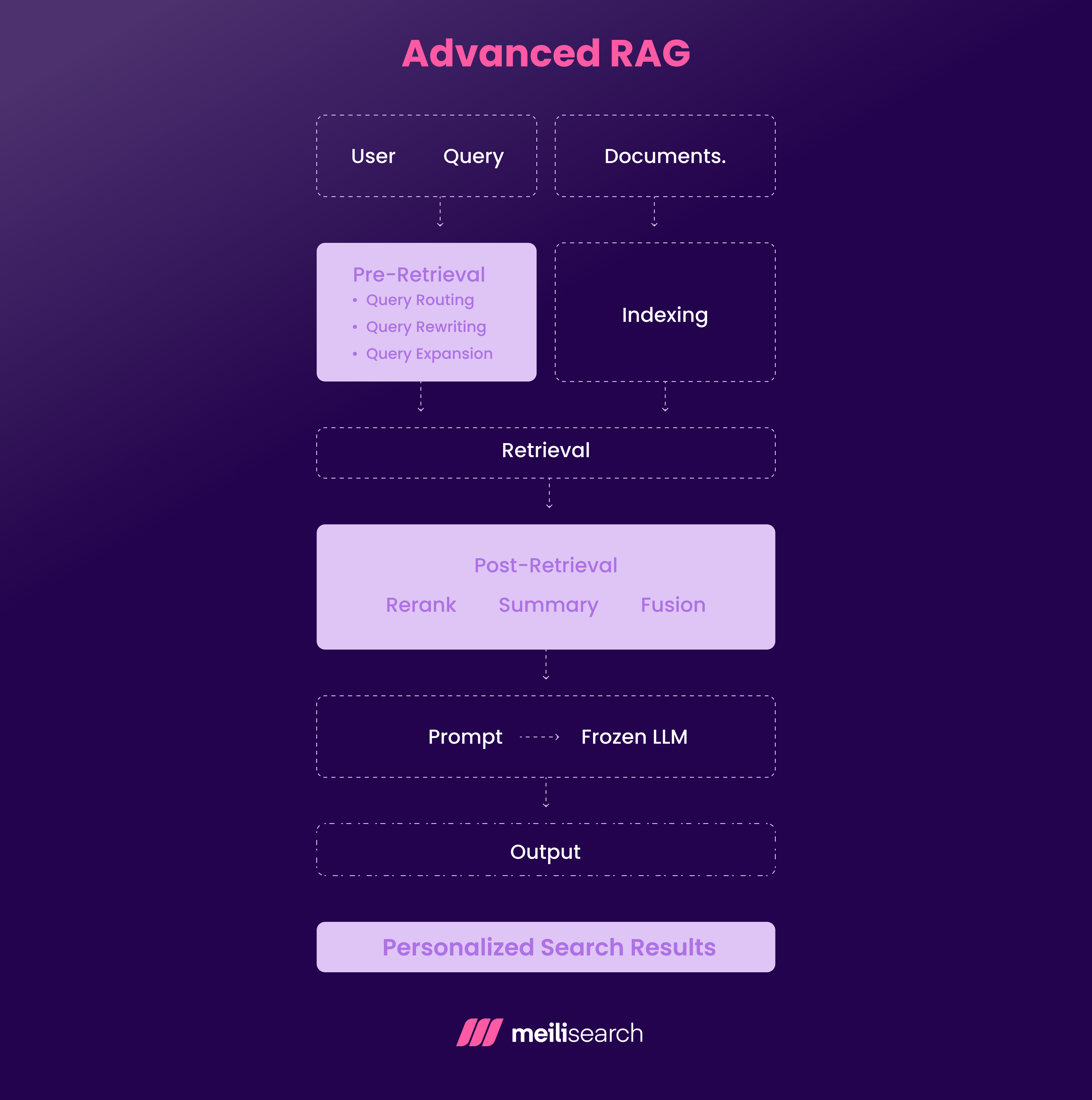
- Pre-retrieval optimization: Before retrieval even begins, the system rewrites user queries to capture better what the user actually means. This helps in matching domain-specific terminology and providing additional context.
- Multi-stage retrieval: Instead of just one, advanced RAG has multiple retrievers. They pull results from various sources to cover a broader range of information types. The sources can be databases, vector stores, and even APIs.
- Post-retrieval reranking and filtering: The process of reranking serves as an eliminator for the less relevant responses. It uses LLM scoring to deliver the most appropriate answers.
- Auto-merging and context pruning: Overlapping or repetitive text is merged, and low-value content is removed before generation.
- Response generation: The final, filtered context is passed to the generation model for coherent, grounded answers.
As you can tell, these added layers serve to fine-tune and improve the generated responses to the users’ liking.
Let’s take a look at the major differences between these two RAG approaches.
What is the main difference between naive and advanced RAG?
The main difference between naive RAG and advanced RAG is in precision and control.
Naive RAG has a single retriever loop, whereas advanced RAG includes multiple layers to generate the most accurate responses.
Naive RAG is the best choice when you want speed and simplicity, while advanced RAG will serve you the best when it comes to optimizing for a highly accurate and reliable RAG pipeline.
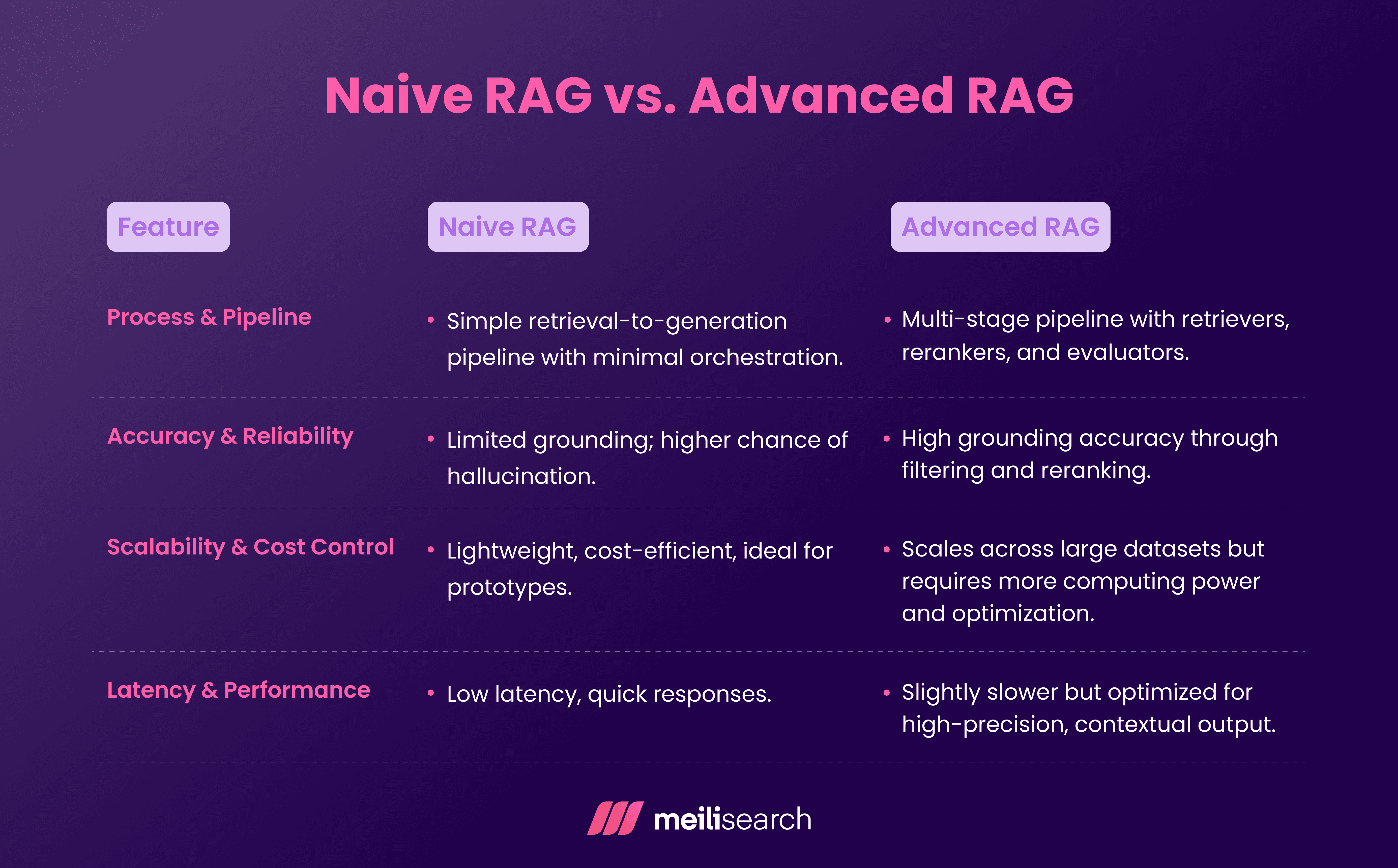
Naive RAG is suitable for quick experiments or internal tools, while advanced RAG is built for enterprise-grade deployments that demand the next level of precision and trust.
What are the benefits of naive RAG?
For teams that are starting out, there is no better starting point than naive RAG. It can be your first step into experimenting in this domain:
- Super simple: For naive RAG, all you need is a retriever, an embedding model, and a generator. This simplicity makes it ideal for quick deployments or creating a proof of concept.
- Top-tier speed: Since there’s minimal pipeline orchestration, the responses from naive RAG are quick and have almost non-existent latency.
- Easy on the wallet: Thanks to fewer API calls and pretty much zero reranking layers, it’s budget-friendly.
- Maintenance isn’t a chore: Since the architecture is so lightweight, you only need to maintain or tune a limited number of moving parts.
- Flexible: The flexibility of naive RAG means it works well in question-answering applications, such as chatbots, where accuracy isn’t a significant issue.
What are the benefits of advanced RAG?
Advanced RAG provides a detailed level of control that naive RAG could never achieve:
- A monumental jump in accuracy: Thanks to extra layers, such as reranking, filtering, and query rewriting, advanced RAG generates responses that meet the user’s needs much better than naive RAG responses.
- Highly relevant: Through multi-stage retrieval, advanced RAG ensures that users receive only the most relevant chunks within the desired context.
- Scalability on point: Advanced RAG's modular design was specifically created to support large-scale vector databases and hybrid retrievals. It can handle enterprise workloads with ease.
- Fewer hallucinations: Continuous feedback loops and evaluation metrics help improve the quality of responses over time.
- A ton of flexibility: Since it handles varied data sources, advanced RAG offers a significant amount of flexibility, allowing it to work without retraining the LLM repeatedly.
In short, advanced RAG is the perfect fit for highly critical AI RAG applications and setups that process complex queries.
To master RAG and its various types, feel free to check out our official guide.
What are the limitations of naive RAG?
Naive RAG’s simplicity makes it easy to start with, but it limits its ability to scale or deliver consistently accurate results over time:
- Low precision: Since it retrieves documents only based on similarity scores, there’s a considerable potential for inaccurate responses.
- Limited recall: Naive RAG might even miss relevant information entirely because it lacks an element of reranking or query refinement.
- Outdated information: Since retrieval isn’t dynamically refreshed or filtered, responses might include data that’s irrelevant or stale.
- Room for hallucinations: The LLM might misinterpret the retrieved information, which could lead to hallucinations.
- No feedback mechanism: The absence of evaluation loops or retraining signals results in no improvement over time.
These issues make naive RAG best suited for experimentation rather than production environments where precision is required.
What are the limitations of advanced RAG?
Advanced RAG offers scalability and a trust factor, but it comes with inevitable trade-offs.
- Extremely high complexity: The many optimization layers increase advanced RAG’s complexity to a point where considerable engineering effort is required to maintain it.
- It requires resources: When handling larger pipelines, advanced RAG requires more computing power, memory, and API calls. These costs can add up over time.
- Risk of overfitting: Being overly specific limits how well language models can perform across different data types or industries.
- Harder to evaluate: To track retrieval precision and hallucination rates, you need to have complex benchmarking setups in place.
While advanced RAG addresses many of the weaknesses of naive RAG, it requires significant resources to maintain its optimal state.
When should you use naive RAG?
Naive RAG is the perfect fit if you want to prototype early-stage LLM applications or test prompts.
Smaller projects, such as chatbots, internal knowledge bases, or proof-of-concept demos, benefit greatly from the speed and simplicity that naive RAG brings. It is also a good fit when data volume is small and latency must stay low, such as in local or offline use cases.
However, naive RAG’s lightweight design means you have to give up on precision and scalability.
When should you use advanced RAG?
Are you working in a domain where there’s simply no compromise on precision and accuracy? Then, advanced RAG is your choice.
It’s ideal for enterprise-grade systems, customer-facing chatbots, and domain-specific assistants. It’s a particularly good fit for medical knowledge platforms or legal research tools. It’s also perfect for large datasets with hybrid retrieval systems.
What are common applications of naive RAG?
Naive RAG is used where speed and simplicity are more important than any other factor. Let’s see a few typical applications below:
- FAQ chatbots: In FAQ chatbots, naive RAG helps generate quick responses from internal documents without requiring complex reasoning.
- Internal search tools: Naive RAG helps teams access relevant snippets from wikis, manuals, or emails using simple embeddings.
- Knowledge retrieval systems: Naive RAG is used in systems that require the quick fetching of facts or short answers from a predefined dataset.
- Prototype assistants: Another everyday use of naive RAG is in prototype assistants that developers like to test before scaling with different RAG models.
- Customer support portals: Naive RAG helps surface the most relevant articles or troubleshooting guides without requiring full-text generation.
What are common applications of advanced RAG?
For high-powered systems that thrive on high accuracy and minimal hallucinations, advanced RAG is the go-to choice:
- Enterprise chatbots: Advanced RAG is used in enterprise chatbots that provide well-researched answers across departments by combining various internal knowledge bases.
- Legal and compliance assistants: You’ll find advanced RAG in legal and compliance assistants, where you need accurate retrieval or citation of verified information.
- Medical research tools: The medical field can’t compromise on accuracy. Advanced RAG is used to provide insights from clinical studies in medical datasets.
- Customer support automation: Advanced RAG is also used to combine semantic search and retrieval with LLM reasoning to provide detailed responses in customer support.
- AI research assistants: Advanced RAG supports data scientists and engineers, especially when they handle repositories and experimental data.
All in all, when the environment is complex or data-heavy and regulated, the advanced RAG framework provides the relevant accuracy and transparency that’s needed.
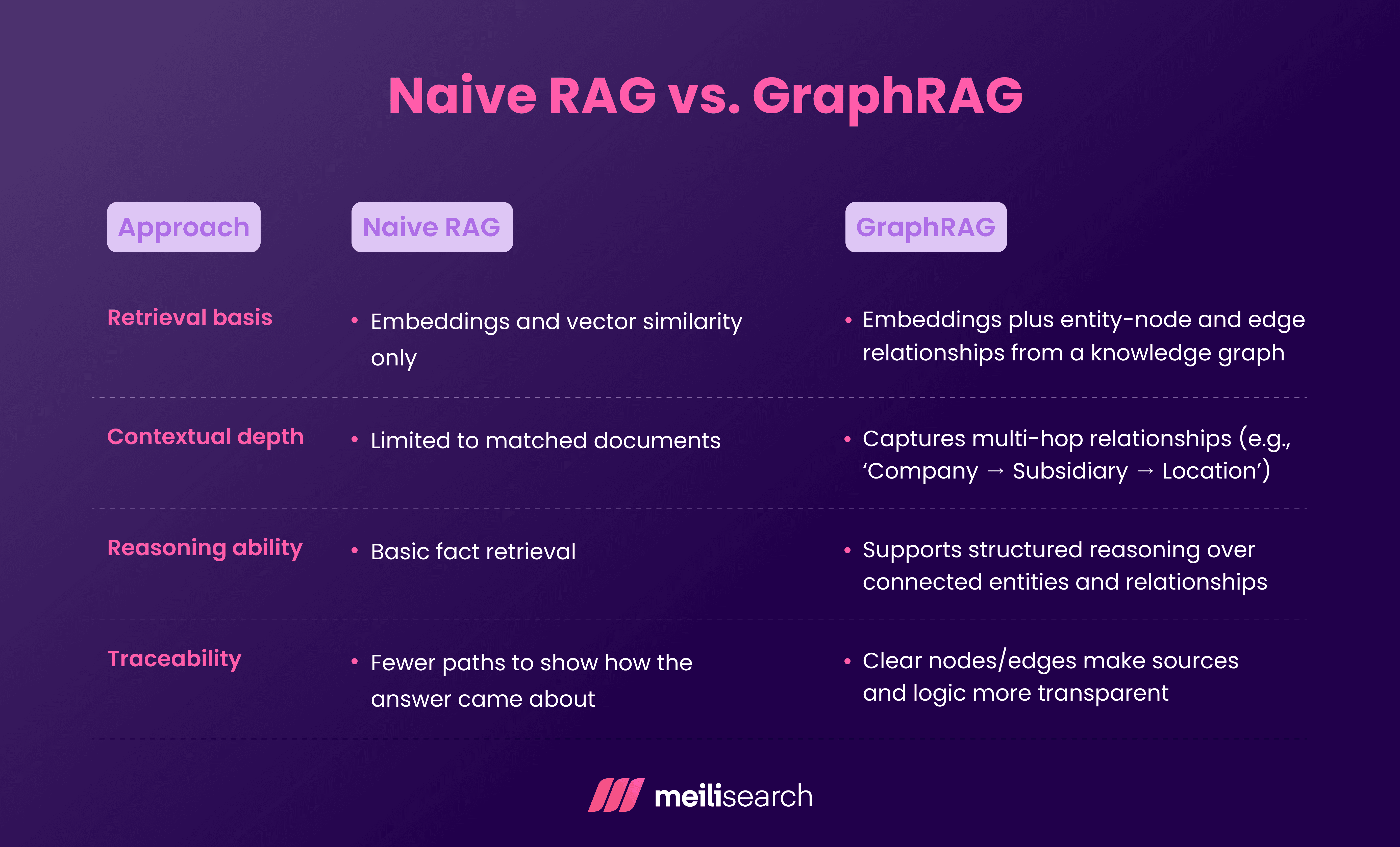
How does naive RAG compare to GraphRAG?
The main difference between naive RAG and GraphRAG is that naive RAG treats documents as isolated chunks for retrieval purposes.
GraphRAG, on the other hand, connects various entities and relationships within a specific context to provide deeper reasoning and traceability.
Now, we’ll move to some examples of advanced RAG techniques.
Examples of advanced RAG techniques
Advanced RAG has its own set of layers and retrieval techniques that help improve the accuracy and precision of responses.
Many of these techniques are outlined in our in-depth article on advanced RAG techniques:
- Dynamic chunking: In this process, the documents are broken into contextually coherent pieces rather than fixed blocks. This provides a significant improvement in retrieval quality, eliminating unnecessary noise.
- Query rewriting: This refers to the process of rewriting user input before search, so that the retriever surfaces better-matched context. It can be through synonyms, clarification, or similar.
- Reranking and filtering: After the initial retrieval, results are rescored and low-value items are removed. The only way forward is a high-quality response.
- Hybrid retrieval: This type of retrieval gives you broader recall and increased precision, which is particularly useful for mixed-type data.
- Feedback loops and context distillation: In naive RAG, there are no feedback loops. In advanced RAG, however, the system logs user outcomes and refines chunks over time to improve response accuracy.
Now, we’ll see how you can evaluate naive and advanced RAG setups.
How to evaluate naive vs. advanced RAG
To evaluate each of these systems, consider how they perform in terms of accuracy, answer quality, and latency.
Naive RAG generally scores high on speed and simplicity, whereas advanced RAG prioritizes factual grounding and user trust through re-ranking and improved retrieval layers.
For a detailed explanation of evaluation frameworks and metrics, explore our RAG evaluation guide, which breaks down structured methods to assess retrieval and generation quality.
Next, we’ll look at best practices for upgrading from naive to advanced RAG.
What are the best practices for moving from naive to advanced RAG?
So, how can you methodically transition from a naive RAG to an advanced RAG system? It’s all about maintaining structure without overcomplicating the stack.
You can start with the following steps:
- Audit your current pipeline: Identify all latency or accuracy issues before adding a layer of complexity.
- Adopt modular upgrades: Add updates one step at a time. For instance, start with query rewriting, then reranking, and then hybrid retrieval. Track the progress at each step.
- Implement continuous evaluation: Ensure that you keep track of hallucination rates, accuracy, and latency.
- Optimize data and chunking: Refine document splitting and embedding quality.
- Automate feedback loops: Leverage user interactions to refine retrieval scoring and query understanding algorithms.
Meilisearch is the perfect companion for you in this transition process. It helps by offering an OpenAI-compatible /chat** **API that bundles query understanding, structured retrieval, and generation in one call. This helps avoid heavy infrastructure.
You can also view our picks for the best RAG tools on the official page.
Choosing the right approach in the naive RAG vs. advanced RAG journey
Naive RAG is for teams that are just starting with experimentation and want to test the RAG waters before moving to full-scale deployments.
Advanced RAG serves better in accuracy-critical domains and large-scale deployments.
The right choice depends on your goals. If your focus is on testing and agility, start with a naive approach. If your product requires precision, resilience, and scalability, consider adopting advanced RAG techniques.