How document indexing works, methods, implementation, & more
Learn what document indexing is, how it works, and why it’s key to fast, accurate information retrieval and efficient document management across industries.
In this article
Document indexing enables quick searching and retrieval of digital documents. In this guide, we will show you how to build an indexing system that supports fast search and lets you access reliable information quickly.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- What exactly document indexing is and how documents become searchable.
- The importance of indexing and why it is critical for accessing reliable information.
- The types of industries that rely on indexing.
- The workflow behind document indexing, with explanations for each step.
- The key difference between scanning and indexing, and when you should use one over the other.
- Common indexing methods, such as field-based indexing, metadata indexing, and full-text indexing.
- The unique set of challenges that you can expect to encounter in document indexing.
- How you can build a real-time indexing system with the help of Meilisearch.
Let’s start with the first step: what document indexing actually is.
What is document indexing?
Document indexing is a structured organization of digital documents based on information such as keywords, metadata, and other relevant fields. The sole purpose is to ensure that these documents can be found quickly when needed.
Document indexing is especially important for industries such as healthcare, where specific documents (patient records, reports, contracts, etc.) need to be immediately pulled from vast amounts of data.
Why is document indexing important?
Document indexing is important because it simplifies information retrieval. Without it, teams would waste a lot of time having to review digital documents themselves, without automation, and being hampered by manual indexing errors.
When you eliminate human error in favor of information-based indexing based on metadata, names, dates, or other elements, you improve your bottom line. Information is instantly available, and no one spends more time than necessary finding exactly what they need.
So which industries benefit most from document indexing? Let’s see that below.
What industries benefit most from document indexing?
Many industries rely heavily on large volumes of digital files and would greatly benefit from a fast and simple means to access relevant information.
These industries include:
- Legal: Law firms use indexing to sort and organize contracts and case files to keep up with court records. It also helps them not lose any case-critical documents.
- Healthcare: Hospitals use document indexing to keep track of patient charts, lab reports, and insurance forms.
- Finance: Banks can’t compromise on invoices, account numbers, and other digital information, so they rely on document indexing for records management.
- Education: The need to manage enrollment forms, transcripts, research materials, and attendance sheets makes document indexing essential for educational facilities.
- Government: Agencies often index permits, licenses, and public records so the public, as well as government offices, can access them.
How does document indexing work?
Document indexing works by identifying key information in digital documents. This information is then used to store these digital documents in an organized indexing system. For instance, we can use keywords, tags, and metadata to make indexed documents easy to search.
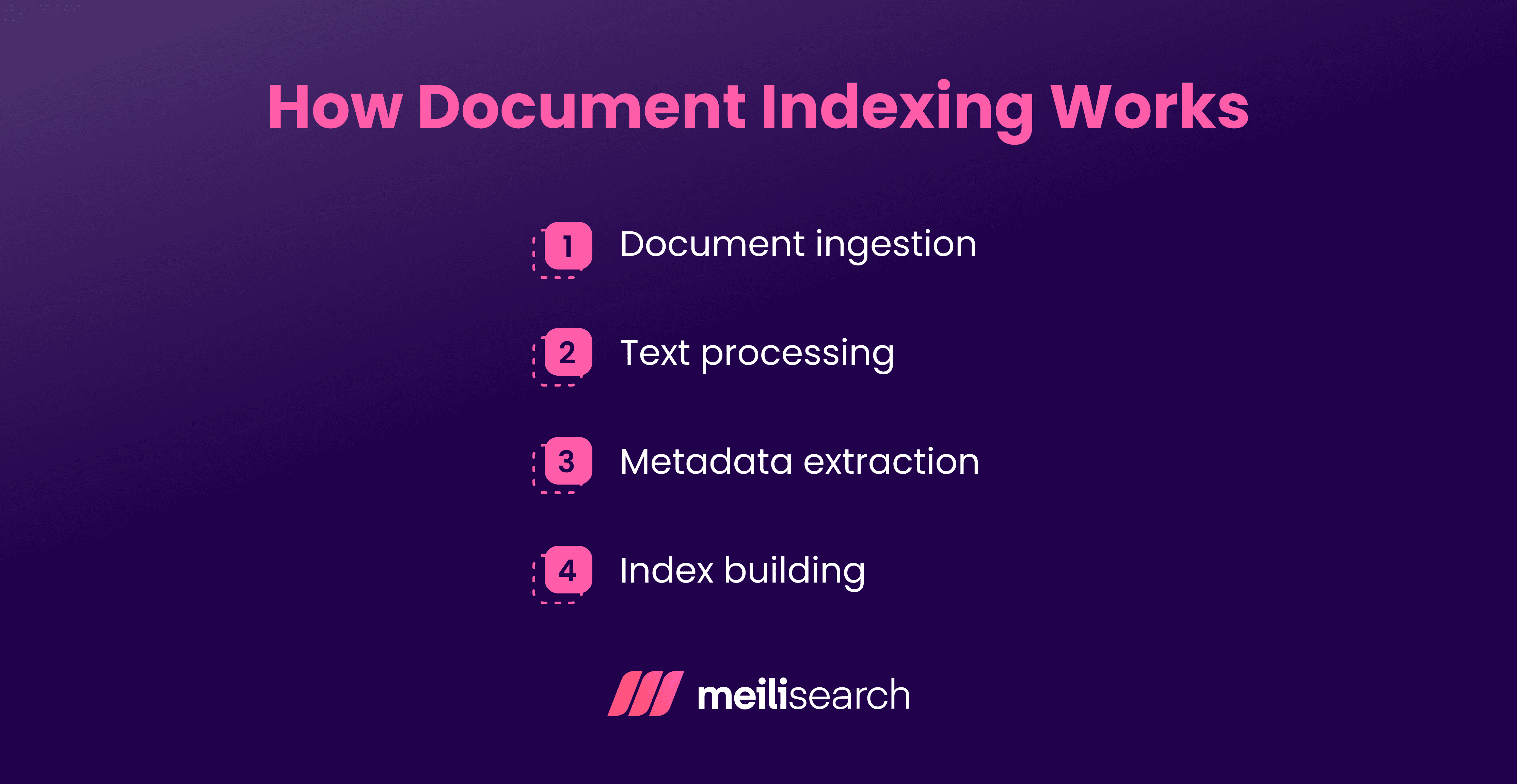
1. Document ingestion
The first step is to gather all documents you want indexed. They can be collected from websites, external databases, internal knowledge bases, etc.
2. Text processing
The text is cleaned and prepared so that the search engine can understand it. This can include processes such as lowercasing letters, removing stop words such as ‘and’ and ‘the’, stemming or lemmatization (reducing words to their base form), and similar.
3. Metadata extraction
Key information, or metadata, is identified in each document. Key information can be specific keywords, names, barcodes, dates, or similar.
4. Index building
Finally, the search catalog is built based on the extracted metadata. When a user types in a query, the system pulls up relevant documents in the blink of an eye.
How is document indexing different from document scanning?
Document indexing and document scanning work together, but they solve different problems in information management.
The role of scanning is to convert paper documents into digital documents. Indexing is the step that comes after scanning.
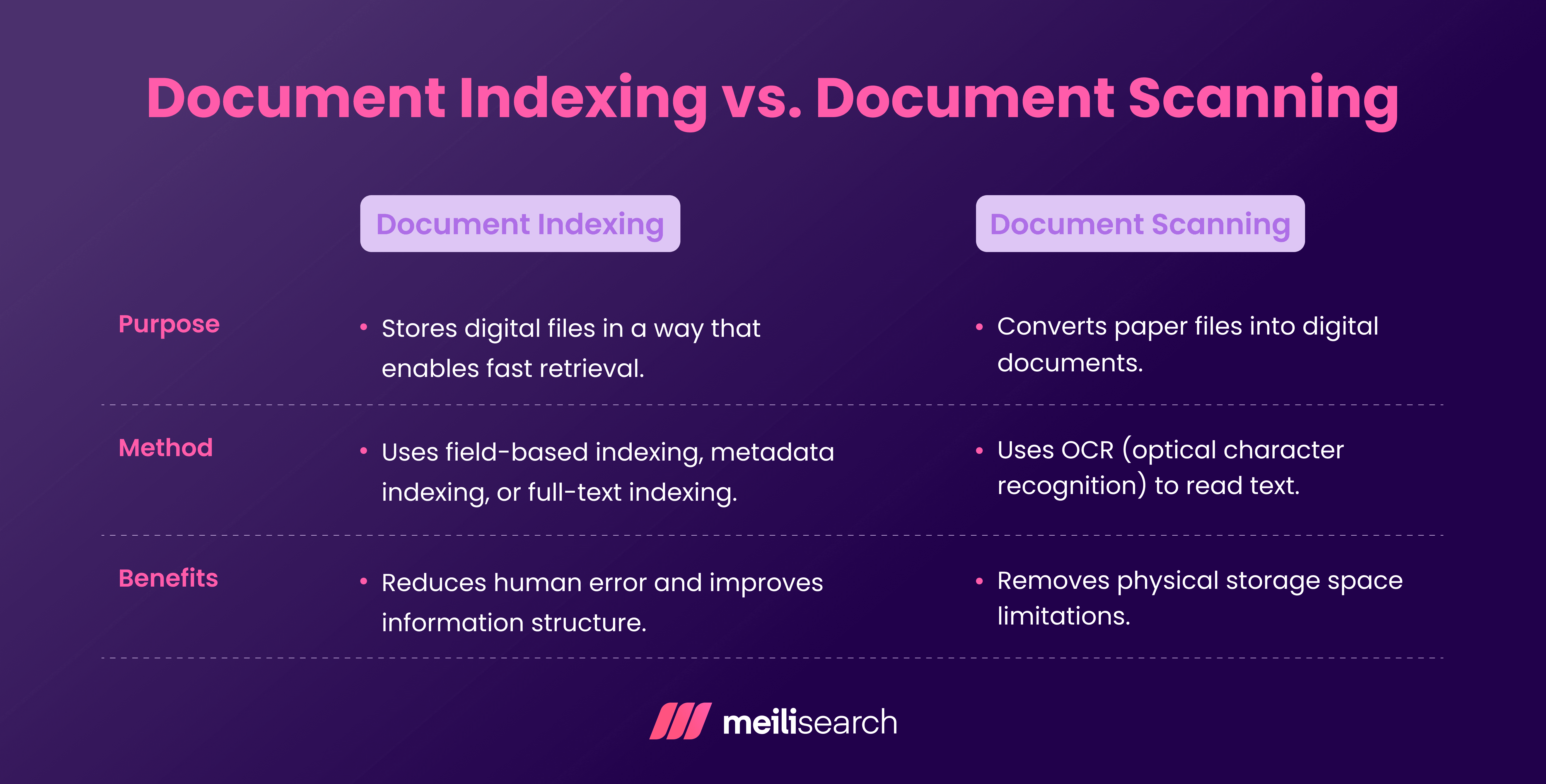
In short, scanning digitizes documents, and indexing makes them findable.
What are common methods of document indexing?
Document indexing can be done in a variety of ways, depending on the types of documents, workflow needs, and the volume of digital files being managed.
- Manual indexing: A person enters document information and organizes everything by hand. Manual indexing offers control but it takes too much time, and there’s always the possibility of human error.
- Metadata-based indexing: As the name suggests, the documents are organized using metadata elements, such as file name, authors, dates, etc.
- OCR-based indexing: Text is extracted from paper documents or scanned documents using optical character recognition. It helps turn paper into digital documents that can be indexed automatically.
- Automated indexing: Algorithms or systems apply tags or full-text indexing without any manual work. This works well when dealing with large volumes of document-based data.
What types of information are used for indexing?
Using specific data points makes it easier to organize files and filter results, just as arranging your closet by color makes it easier to find items you want.
Common types of information used for document indexing include:
- Keywords: The phrases that indicate the main subject of the document.
- Metadata: Specific details of the document, such as the file name, author, title, etc.
- Document type: The classification labels of documents, such as invoices, reports, forms, etc.
- Identifiers: Values like an invoice number, account number, or customer ID.
- Dates: Creation, modification, or event dates for easy sorting.
- Tags or categories: Assigning tags or categories helps group related files together.
- Extracted text: The type of content that is captured through full-text indexing or OCR for deep search.
Based on this set of data points, it becomes relatively easy to retrieve accurate information from the indexing system.
Let’s look at how indexing supports information retrieval.
What is the role of indexing in information retrieval?
Indexing is the backbone of information retrieval because it provides a structured map of digital documents. By storing keywords, different identifiers, and metadata, it groups relevant information together.
Document indexing eliminates the need for manual scanning and strengthens the search functionality across databases and document management systems. If your indexing process is clean, even extensive collections cannot hinder retrieval.
Now, let’s examine the challenges that go hand in hand with document indexing.
What challenges are common in document indexing?
Document indexing can become overwhelming when organizations have to manage large volumes of digital files and rely on unoptimized processes. These issues affect retrieval accuracy and long-term information management.
Here are some of the most common challenges teams face:
- Inconsistent tagging: Different teams label documents differently. As a result, the indexing system becomes unreliable. The fix for this is a set of standardized tags, categories, and vocabulary.
- Human error: Manual entry leads to mistakes such as missing fields, typos, and mislabeling. The best way to fix this is to shift toward automated indexing.
- Poor metadata quality: Weak or incomplete metadata makes document retrieval difficult. Clear rules for required fields, such as dates or invoice numbers, significantly improve the structure.
- Unscannable or low-quality documents: When the quality of scanned documents is poor, even the best OCR cannot make them readable. Better scanning tools for data extraction should help here.
Let’s see how automated document indexing works with Meilisearch in real environments.
How automated document indexing works with Meilisearch
Meilisearch eliminates the need for manual work, replacing it with fast, optimized, searchable indexes in real time. It extracts key document attributes and organizes them into an optimized indexing system.
Here are the main steps to indexing your documents using Meilisearch:
1. Import and prepare your documents
The first step is to load the documents into your workflow. These documents can come from various sources, such as APIs, storage buckets, scanned documents, or even existing databases. Meilisearch accepts JSON, so there’s no problem in pushing the field titles, dates, tags, etc.
_curl \_ _-X POST 'http://localhost:7700/indexes/documents/documents' \_ _-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \_ _--data-binary @documents.json_
2. Extract key fields and metadata
Extraction is key for identifying attributes within each file, such as metadata, keywords, categories, and so on.
For example, if a document comes from OCR, the extracted text instantly becomes a part of full-text indexing.
Meilisearch categorizes files and enriches indexed documents to improve relevant information retrieval.
_{_ _"id": "doc_01",_ _"title": "Insurance Claim Form",_ _"date": "2024-01-19",_ _"account_number": "298231",_ _"content": "Full OCR text goes here..."_ _}_
3. Index documents and enable search features
Indexing uploads the enriched documents into Meilisearch. Immediately, the engine builds indexes and applies features, enabling various search functionalities such as typo tolerance and synonyms.
_curl \_ _-X PATCH 'http://localhost:7700/indexes/documents/settings' \_ _-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \_ _--data '{_ _"searchableAttributes": ["title", "content"],_ _"filterableAttributes": ["date", "account_number"]_ _}'_
4. Apply custom ranking and optimize relevance
Now comes the step that defines ranking rules based on the priorities you set, such as dates, status, or file names. Different types of documents require different priority levels.
_curl \_ _-X PATCH 'http://localhost:7700/indexes/documents/settings' \_ _--data '{_ _"rankingRules": [_ _"words",_ _"typo",_ _"proximity",_ _"attribute",_ _"sort",_ _"exactness"_ _]_ _}'_
5. Keep the index updated in real time
Lack of index updates can cause bugs and inconsistencies. Meilisearch supports incremental updates so that any new or modified documents become searchable immediately. This takes away time-consuming manual updates and keeps business operations running smoothly.
Thanks to these real-time updates, document management systems always reflect the most current data.
_curl \_ _-X POST 'http://localhost:7700/indexes/documents/documents' \_ _--data '[{ "id": "doc_01", "status": "updated" }]'_
Document indexing in modern information systems
Modern systems rely heavily on document indexing because they require up-to-date information and accurate retrieval. Scaling is also a big reason automated indexing has flourished in recent years.
Through effective indexing, you can optimize all document-related processes for your business, including search accuracy, fast access across workflows, and document management.


